10 Steps to Rubber Manufacturing:
1) Polymerization
2) Isolation
3) Compounding
4) Extrusion
5) Molding
6) Flash Removal
7) Post Curing
8) Finishing & Inspection
9) Cleaning
10) Packaging
Polymerization
The beginning step for elastomers is the polymerization of the backbone and cure-site monomers. This is typically done by large chemical companies such as Du Pont, Dow, GE, Ausimont, Daikin and Dyneon. Common techniques are emulsion, microemulsion, and suspension polymerization. Polymerization combines two or more process gases (monomers) into an aqueous environment and under specific temperature and pressure conditions connects the individual monomers into the desired polymer. Initiating agents, buffers and other chemicals may be added to the polymer reactor to achieve the desired chemical properties and polymerization dynamics.
Types of Polymerization Reactions
- 1. Condensation Polymerization-
yields polymers with repeating units having fewer atoms than the monomers from which they are formed. This reaction generally involves the elimination of small molecules such as H2O or HCl.
- 2. Addition Polymerization
- 3. Chain Polymerization/Free Radical Polymerization-
- A. Initiation: formation of free radicals by scission of a single bond (homolysis), or by the transfer of a single electron to or from an ion or molecule (redox).
- B. Propagation: growth of macromolecular structure.
- C. Chain Transfer and Termination: completing the polymerization step.
Types of Chain Polymerization Methods
Bulk Polymerization-
involves only the monomer and a monomer-soluble initiator.
- Solution Polymerization-
a solvent lowers the viscosity, assisting heat transfer and reducing the likelihood of auto-acceleration. - Suspension Polymerization-
reaction mixture is suspended as droplets in an inert medium. Polymer particles are produced in the form of beads in the range of 0.1 to 2 mm in diameter. - Emulsion Polymerization-
the initiator is not soluble in the monomer but soluble only in the aqueous dispersion medium. Polymer is produced in the form of a latex with particles in the range of 0.05 to 1 micron.
Isolation
The backbone polymers are isolated (brought out of the emulsion), cleaned and dried.
Chemical agents may be added at this step to isolate the polymer “latex” into a more usable form. Once the polymer is cleaned and dried, the “crumb” polymer is shipped to compounders (or O-ring molders) for mixing.
Compounding (mixing)
The “crumb” polymer is mixed with a cross-linking agent and other functional fillers. The cross-linking agent allows chemical bonds to form between the polymer backbones, thus providing resiliency to the material. Functional fillers include reinforcing fillers, pigments, anti-degradants, acid scavengers and process aids. These ingredients are typically mixed together on a 2-roll mill or other custom mixing machinery.
Extrusion
The sheet compound is extruded into a configuration similar to the desired finished part.
Clean Extrusion
Molding
Most of the elastomeric O-rings used in the semiconductor industry are compression molded. A preshaped form is inserted into a multi-section mold and transferred to a heated press. Under heat and pressure, the elastomer flows into the mold cavities and chemical cross-linking takes place (or begins to take place, depending on the specific elastomer compound). After a period of time ranging from several seconds to several minutes, the parts are removed from the hot molds. Depending on the compound, mold releases are often used. These diluted spray coatings are often a derivative of fluoropolymers, or silicone-based polymers.
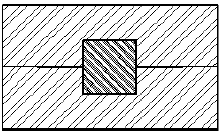
Compression Molding
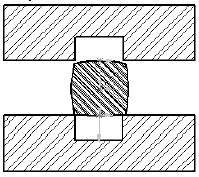
Raw material is inserted
The raw material is compressed with pressure and heat
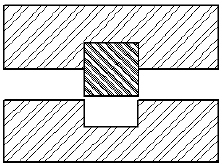
The finished part is released
Injection Molding
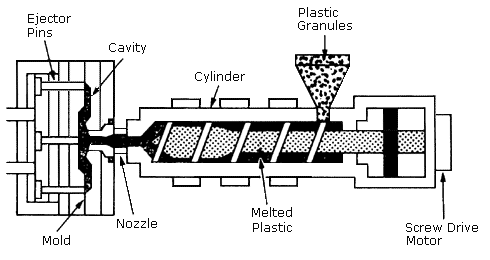
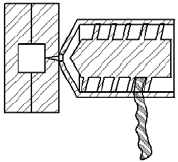
The raw material strip is fed into the barrel
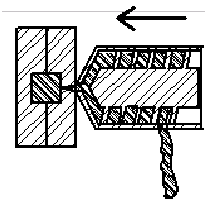
The screw rotates to push the raw material thru
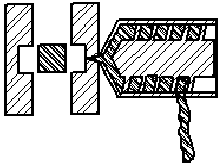
The finished part is released
Transfer Molding
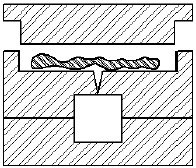
The raw material is fed thru a pot and transfer hole.
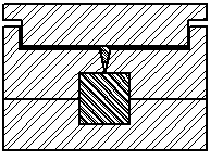
The raw material is compressed with pressure and heat

The finished part is released
Flash Removal
After the parts are removed from the molds, they contain thin “flash” as a result of the elastomer flowing in the multi-section mold. This “flash” is typically removed by exposing the parts to a cryogenic tumbling process. The elastomer is cooled and tumbled, causing the thinner “flash” section to become brittle and break away from the main part. Additional tumbling or handdeflashing may be required on some part designs or compounds.
Curing
Some high-performance elastomers are subjected to a post-curing operation. Elastomer parts are exposed to high temperatures in carefully controlled environments for several hours to complete the curing process. Additionally, this post-curing step removes excess water vapor and volatile process additives, thereby improving vacuum and contamination performance.
Post-cure Ovens
Finishing and Inspection
After the parts are removed from the curing ovens, the parts are again cleaned and inspected to ensure the parts meet the material and dimensional specifications.
Video Inspection Machine
Cleaning
After the parts are inspected, acceptable parts are delivered to the Class 100 clean room for cleaning and packaging. An ultrapure deionized water (UPDI) rinsing cycle removes surface contamination from the parts.
Clean Room
Packaging
Acceptable parts are then counted and packaged, either individually or in bulk, in a heat-sealed clean inner bag. The parts are then packaged in an outer bag, with a complete description of the parts, lot number, the batch and cure date.
Factory Capability:
750 ton compression machine
500 ton compression machine
300 ton compression machine
100 ton compression machine
300 ton vacuum compression machine
200 ton vacuum compression machine
300 ton injection machine
Basler inspection system
Cutter machine
Batch-off cooling machine
Post cure oven
Whizzer machine
Micro-Vu Video machine
Projector machine
Cryogen machine
Roller machine
Kneader
LABORATORY:
RHEOMETER
TENSILE STRENGTH TESTER
HEAT AGING TESTER
COMPRESSION SET TESTER
DUROMETER (HARDNESS TESTER)
FLEX CRACKING TESTER
TEMPERATURE & HUMDITY TESTER
LOW TEMPERATURE TESTER
DISOLOATION METER
DIELECTRIC WITH STANDING TESTER
TEST SOCKET
FLAME TESTER
ELTRACTIVE TESTER
MOONEY VISCOMETER
ELECTRINIC DENSIMETER
OZONE TESTER CHAMBER
HIGH RESISTANCE METER
ABRASION TESTER
TOOLING:
CNC machines